Over the many years of development, Renode, our open source simulation framework, has been successfully used in various contexts, from the development on the smallest microcontrollers to complex, multi-core and multi-node environments, from driver implementation, through full product simulation, to supporting development of complex networking protocols. One example of the latter has been our work to bring Time Sensitive Networking to the Zephyr RTOS, a protocol seeing increased use in aerospace applications, just like Renode itself.

While our main focus has primarily been around Arm and RISC‑V architectures which are the key drivers for current and next-gen embedded systems, Renode also supports less popular architectures where some safety-critical use cases demanded it: embedded X86, OpenPOWER and SPARC.
SPARC in Renode
SPARC, a well established RISC ISA, was supported in Renode almost from the very beginning, related to our work with LEON CPU the aerospace domain.
LEON3 is an open source CPU developed by Gaisler Research (now part of Cobham) in collaboration with the European Space Agency. With SMP support and a focus on fault tolerance, it is well known and loved within the space industry and is often used for mission-critical applications.
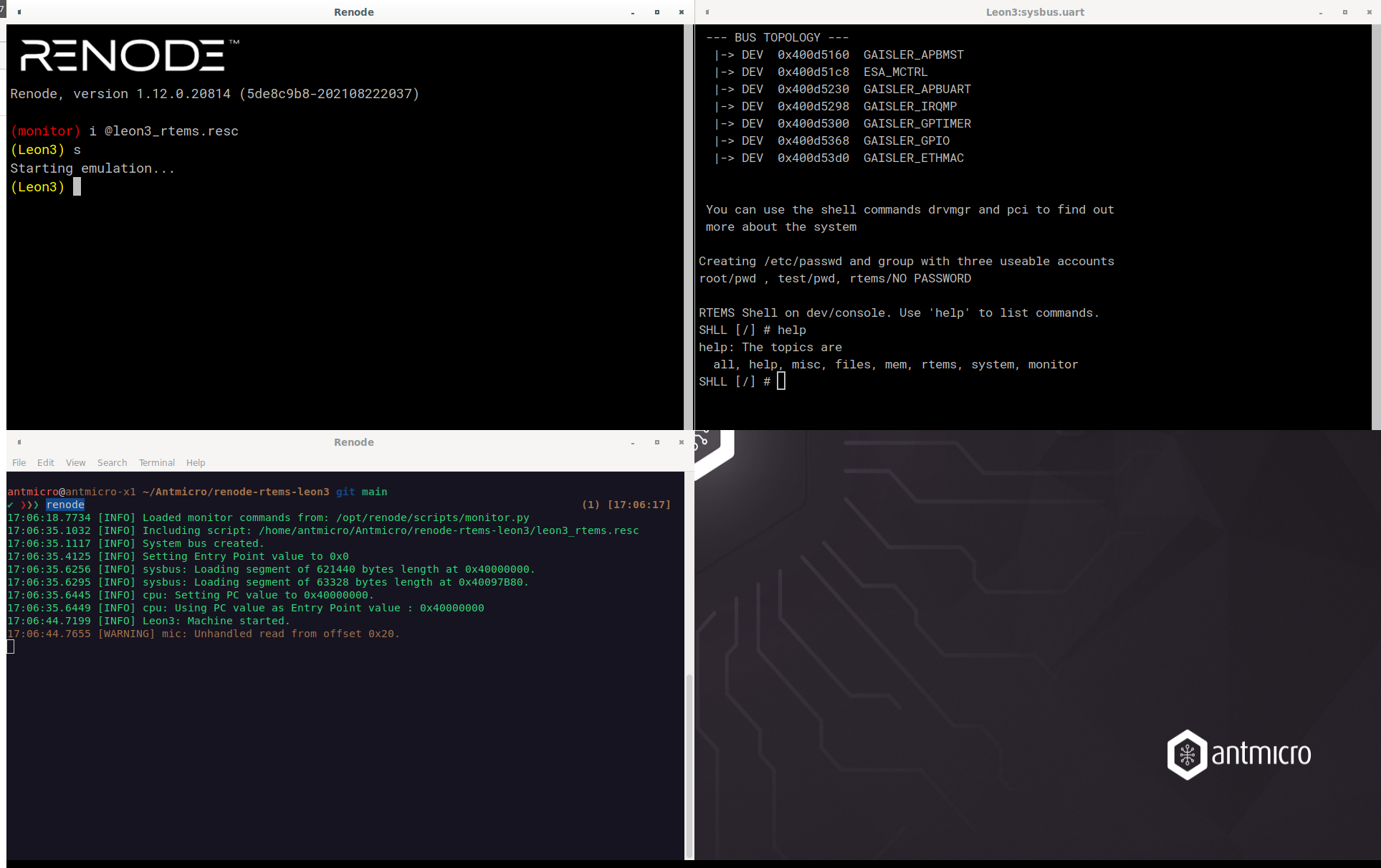
Renode’s support for LEON3 covers not only the CPU but also bus and memory controllers, UART, GPIOs, Ethernet, timer and the interrupt subsystem of a LEON3-based SoC.
Tackling Endianness
An opportunity to revisit our SPARC support occurred when we were asked by the TensorFlow Lite Micro team, our long-time partners, to verify TFLM support for Big Endian architectures related to a space-bound use case of the ML framework. With the majority of modern-day CPUs implementing the Little Endian approach, the opposite is very often more difficult to test.
To help the TFLM team with the issue, we had to improve Renode’s support for SPARC, and Big Endian in general, as well. The improvements included better opcode support, improved GDB integration, Big Endian watchpoints support and more.
Having completed this work, we were able to discover, report and fix endianness handling issues in TFLM. As Renode is used by TensorFlow Lite Micro for testing (both in their own CI and in our dedicated repositories, we plan to include new automated tests for LEON3 in the TFLM tree.
Zephyr support
Our next target to test with LEON3 was the Zephyr RTOS. Zephyr is very often our go-to OS, with its broad feature set, plenty of supported platforms, overall good quality and ease of use. We have recently become a Platinum member of Zephyr and continue to contribute to it in various areas.
A good sample is simple to understand, yet tests many subsystems at once - that’s why we often start with Zephyr’s shell-module sample. To give it a try on LEON3, grab latest Renode and run the provided script. As the next step, we are working on adding support for the GR716-MINI development board, with a hard LEON3 implementation.

Renode in space
Based on Renode’s increasing popularity in safety critical domains, we have recently been invited by Blue Origin to present at the "Open Source for Space" workshop at SMC-IT conference. It was a great event and community dedicated to open source, and we were thrilled not only to present Renode, but also to learn more on topics being covered that are very close to our other work, such as Space ROS.
This presence and the related discussion led us to looking at enabling another piece of space-focused technology which works with SPARC/LEON3 - RTEMS, a very mature open source RTOS. We have worked with it before, but it wasn’t represented in our publicly available Renode demos.
That’s why, prompted by the SMC-IT community, we created a separate demonstration repository to present how we approach building Continuous Integration environments.
This repository includes three things: scripts for building RTEMS for LEON3, the necessary Renode scripts and test cases written in Robot. These are connected together with a GitHub Actions script, showing how easy it is to create automated tests with Renode running on a GitHub CI::
- name: Run tests
uses: antmicro/renode-actions/test-in-renode@main
with:
renode-version: 'latest'
tests-to-run: 'leon3_rtems.robot'Open source for transparency and security
These latest developments highlight Antmicro’s dedication to push the aerospace industry forward. Over the years we have created both hardware platforms, FPGA IP and software that has been sent to space, and Renode fits this picture nicely. With its ability to co-simulate platforms using native models and Verilog components, Renode can serve as a great development tool on every step of product development in aerospace applications.
To learn more about Renode, please visit its homepage and look at the introductory slide deck. We offer commercial support and engineering services helping apply Renode in practice - to request those, reach out to us at support@renode.io and let us know about your use case.