Dec 19
2025

Renode allows you to emulate multi-core platforms, executing code on each core in isolation from one another, in parallel. However, in Symmetric Multi-Processing (SMP) architectures, the CPUs can communicate using various mechanisms, e.g. atomic instructions. Renode implements these mechanisms, but the extra synchronization between cores comes at an additional cost in processing time. Read more
Dec 4
2025
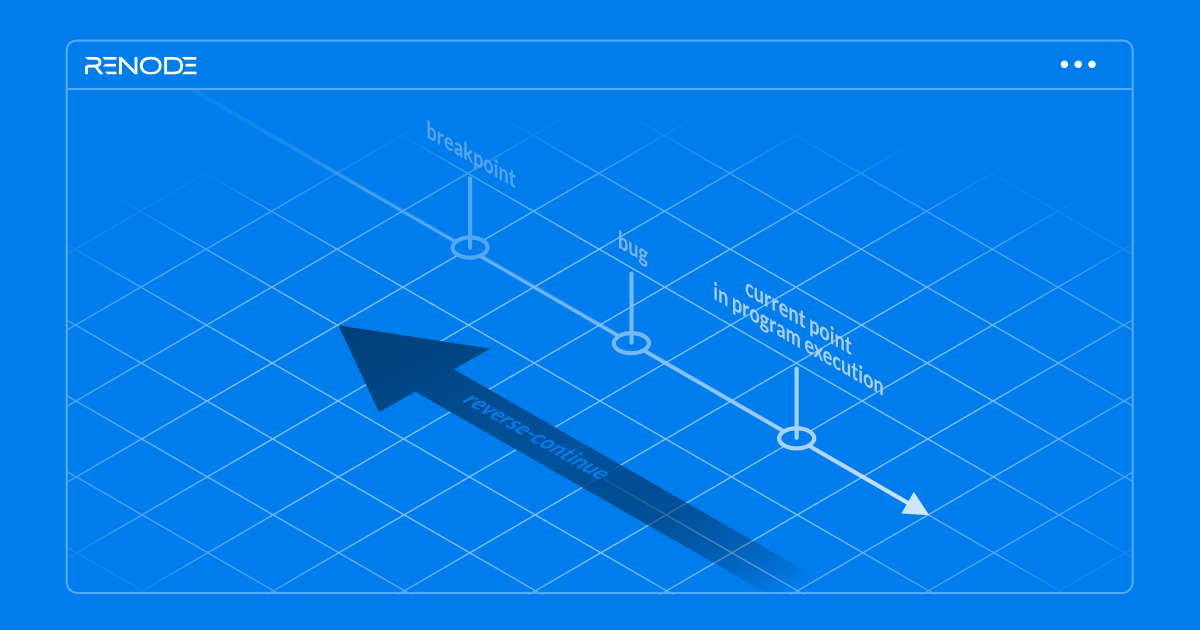
When debugging software, if you step over the code past your region of interest, usually you need to restart the whole process, which takes time. However, by recording the execution of a program and then "rewinding" and "replaying" it, you can go back to the point just before the bug you're analyzing occurred, examine the code, and identify the cause of the bug. This approach, called reverse execution, makes debugging easier and more accurate, as you can focus on a specific piece of code and go backwards and forwards as many times as necessary. Read more
Nov 20
2025

In previous years, we described how Renode support for the Armv8-A CPU architecture profile was enhanced for end-to-end Linux support, and how virtualization can be added for Armv8-R as exemplified by the Cortex-R52 CPU. Now, Antmicro has modeled a System Memory Management Unit (SMMU), which translates virtual addresses into physical ones for platforms running on Armv8-A and Armv8-R CPUs. As a result, we have enabled the use of Renode to test the drivers of the SMMU, and of I/O devices that use external Input-Output Memory Management Unit (IOMMU) translation. By extension, the SMMU translation process itself is also tested for these CPUs and devices. Read more
Nov 6
2025

The open source Bazel build system provides hermetic build environments, facilitating reproducible, controllable builds, with local and distributed cache. This approach significantly accelerates the build process and provides flexibility and extensibility across a wide range of projects, regardless of the codebase size. Bazel has become especially popular among hyperscalers such as Google who leverage their scale and existing infrastructure to build multiple targets in parallel and cache the artifacts to speed up future builds. Read more
Sep 5
2025

Antmicro's open source Renode simulation framework executes code using binary translation - if you run a Cortex-M target on your typical Linux, you need to translate the Arm-M instruction set to x86-64. However, if you want to simulate an x86 platform and you're running on a host with matching architecture, there should be no need to translate anything - you could just run the code of the guest payload. Read more




